
These costs don’t fluctuate with production volume or sales and must be paid regardless of how the business is performing. This predictability makes them easier to budget for but also creates financial obligations that continue even during slow periods. Not from theft or fraud—but from operating expenses you haven’t properly identified, tracked, or managed. For businesses, these day-to-day costs remain the silent profit killers that few leaders truly understand. Operating expenses are operating expenses typically fully tax-deductible in the year they were incurred.
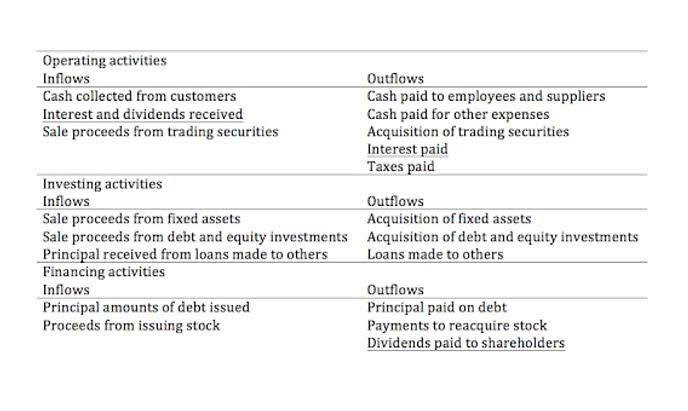
How do capital and revenue expenditures differ?
Operating expenses are essential for the day-to-day functioning of any business. However, effectively managing and reducing these costs can provide a significant competitive advantage and boost profitability. Below are strategies businesses can employ to manage their operating expenses without compromising operational integrity and quality. While operating expenses and capital expenditures are both types of costs incurred by a business, they are distinctly different. Operating expenses are the ongoing costs of running a business, while capital expenditures are one-time costs for purchasing or upgrading physical assets such https://www.bookstime.com/ as property, buildings, or equipment.
- Operating expenses must be ordinary (common and accepted in the business trade) and necessary (helpful).
- Computing this metric is crucial for businesses to determine how much it costs to generate a certain income.
- When employees understand how expenses affect business performance and see their role in managing costs, they become active partners in expense control.
- Creating the right balance between income and expenses can be challenging but yield impressive results.
- FreshBooks expense tracking software can help businesses efficiently track and categorize their operating expenses, such as rent, utilities, insurance, and travel expenses.
Identifying Operating Expenses
A lower ratio indicates that a company is more efficient at managing its operating costs. Variable operating expenses are costs that vary directly with the level of production or sales. These costs increase as business activity increases and decrease as business activity decreases. Examples of variable operating expenses include direct materials, direct labour, sales commissions, and credit card fees.
Calculating Operating Costs

Document all insights and actions in a tracking system to ensure follow-through. While comprehensive expense data is valuable, systems that create excessive administrative burden can become counterproductive. Leading organizations focus on capturing the most decision-relevant expense information while automating data collection wherever possible. By leveraging the insights gained from financial reporting, you can develop more accurate financial projections and strategic plans for your business. Fortunately, you can answer this question by calculating your break-even point. Get free guides, articles, tools and calculators to help you navigate the financial side of your business with ease.

She holds a Bachelor of Science in Finance degree from Bridgewater State University and helps develop content strategies.
- Understanding this distinction can help businesses assess their financial position and make informed decisions regarding investments, loans, or partnerships.
- Therefore it is unreasonable to be used as a metric to compare between firms even if they are in the same industry.
- Operating expenses do not include the Cost of Sales, also known as Cost of Goods Sold (COGS).
- Office supplies – The cost of essentials or materials required for smooth business operations is part of operating expenses.
- In conclusion, calculating operating expenses and analyzing the operating expense ratio are essential tools for assessing a company’s profitability.
- For example, a software company might have higher technology expenses, while a retailer might spend more on inventory storage.
- Companies are required to carry various types of insurance, depending on their industry and location.
- This structure allows stakeholders to evaluate how much it costs to run your core business operations before accounting for other items like taxes or financing costs.
- The tax rules for capital expenditures can vary significantly from those of operating expenses.
- A lower ratio indicates that a company is more efficient at managing its operating costs.
- Operating expenses, often abbreviated as OpEx, are the costs required to run a business’s core operations.
Operating and non-operating expenses are distinct categories that delineate a company’s financial outflows. Non-operating Expenses, as the name suggests, are costs not directly linked to a company’s core business activities. This ratio assesses the efficiency of a company’s spending on selling, general, and administrative expenses in relation to its total revenue.
Fyle’s CoPilot delivers an immediate, AI-driven overview of all employee credit card expenses. Finance teams can effortlessly dissect transactions by category, merchant, project, employee, or department. bookkeeping This empowers you to pinpoint potential risks, operational inefficiencies, and overspending with rapid, intelligent analysis.
